Welcome to AHPS: Best CBSE Board School in India

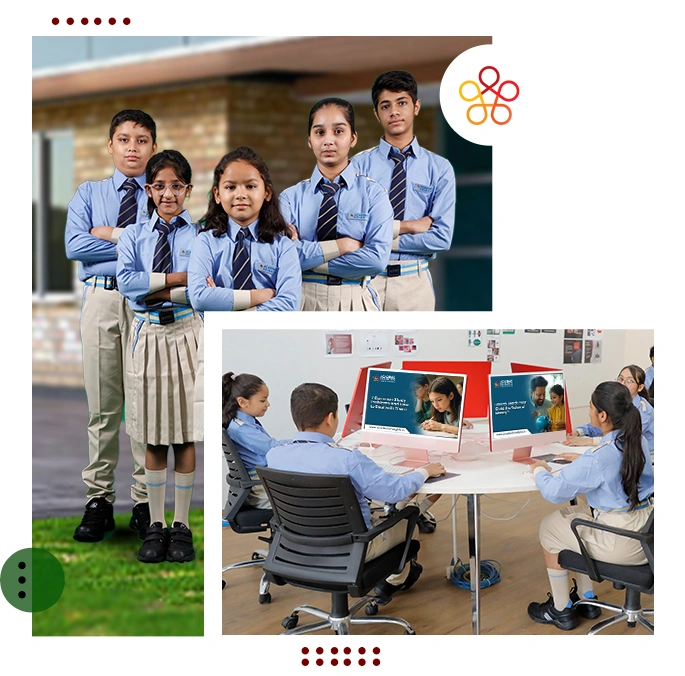
Education at Academic Heights Public School (AHPS) is about more than just academics; it is also about shaping students' lives, instilling values, and preparing them for life after school. Since its founding in 2009, AHPS has revolutionised the K–12 educational experience by providing a smooth transition from preschool foundations to top-notch formal education, establishing it as a best K-12 school and a leading CBSE board school in India.
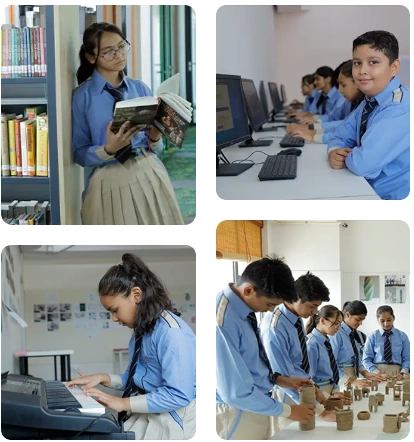
Our commitment to holistic growth is further strengthened with Saina Nehwal, India’s badminton icon, as the brand ambassador of AHPS. Her path of discipline and success reflects the principles we teach our students at the high school. Under the direction of this vision, our campuses have sports areas, innovation-driven labs, smart classrooms, and cultural areas that promote excellence, teamwork, and creativity, all hallmarks of a leading private school in India.
With more than 120 branches across the country, AHPS has established itself as one of India's best high schools, upholding a tradition of excellence. We are often referred to as "a best school with a difference" due to our unique spirit as well as our size. Every AHPSian receives guidance here on how to think independently, behave responsibly, and develop into a global citizen. Every aspect of our academic culture incorporates social-emotional learning and critical thinking to ensure that students are prepared for the challenges of the future. Our commitment to holistic development is what sets us apart as one of the best schools in India.
Developed in accordance with NEP 2020, the SPROUT Curriculum ensures experiential, interactive, and comprehensive learning. As a leading CBSE Board School in India, we foster curiosity while building resilience, intelligence, and character through a focus on STEAM education, debates, quizzes, sports, and the Olympiads.
As a forward-thinking K–12 school, we are dedicated to developing future-ready thinking in all of our students. Our all-encompassing method gives students the values and abilities they need to prosper in a changing world. As a CBSE Board high school, we uphold academic excellence while nurturing critical life skills and a growth mindset in every learner.